Marchantia genome
About
There are two strains in common use by the Marchantia research community: Tak-1 and Cam-1. Both genomes have been sequenced and are searchable.
The Marchantia genome is small (280Mbp) with 8 autosomes and 1 sex chromosome. The genetic redundancy is low, with most of the major gene families represented by a single or a few orthologues. There are 398 transcription factors.
MarpolBase
The genome of M. polymorpha Tak-1 strain has been published by the M. polymorpha community sequencing effort, Bowman et al, 2018. There are about 20,000 loci in the Marchantia genome.
More information in the Genome Database for Marchantia polymorpha, with genome browser view, gene nomenclature and many more tools.
MarpoDB
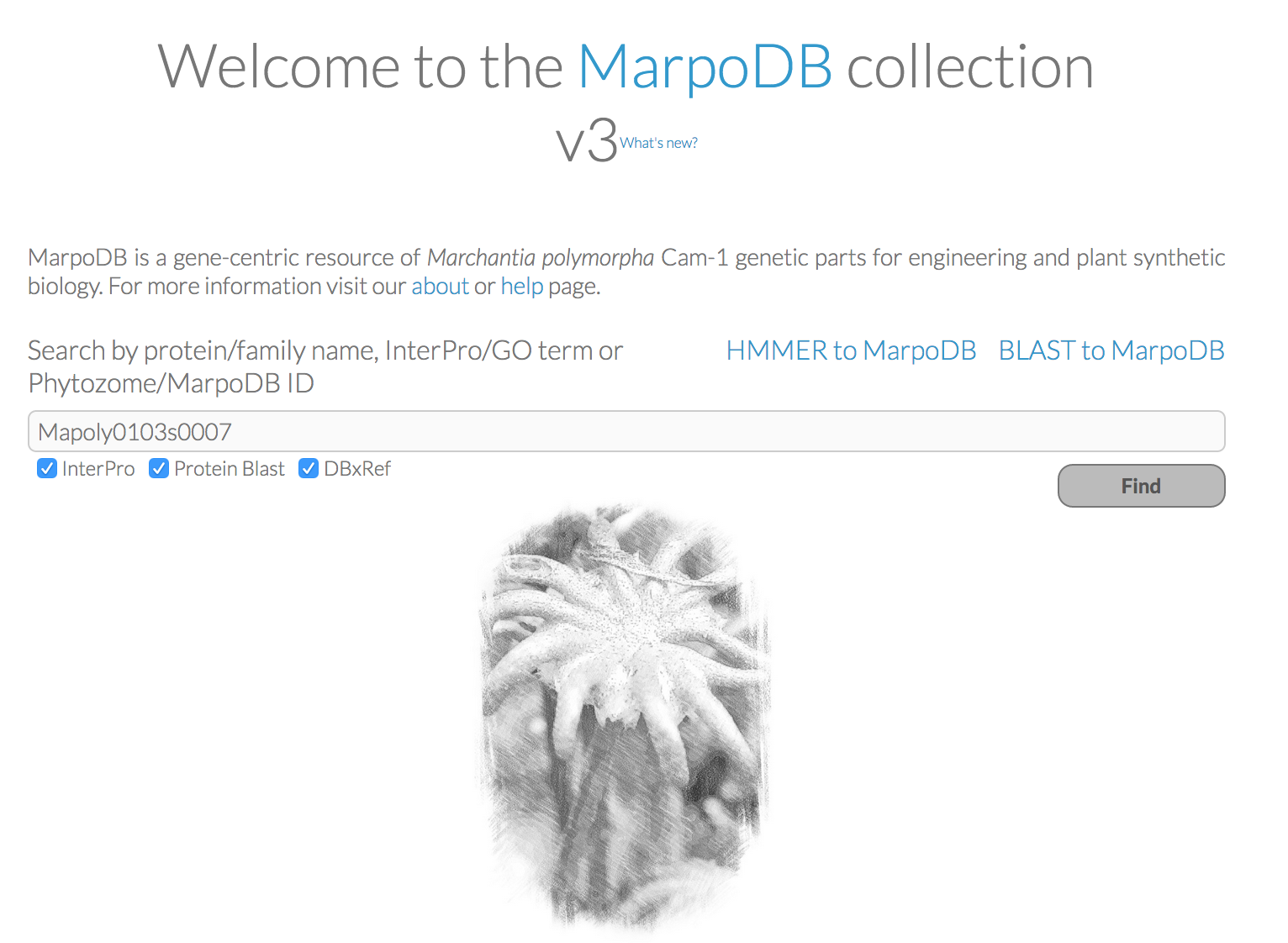
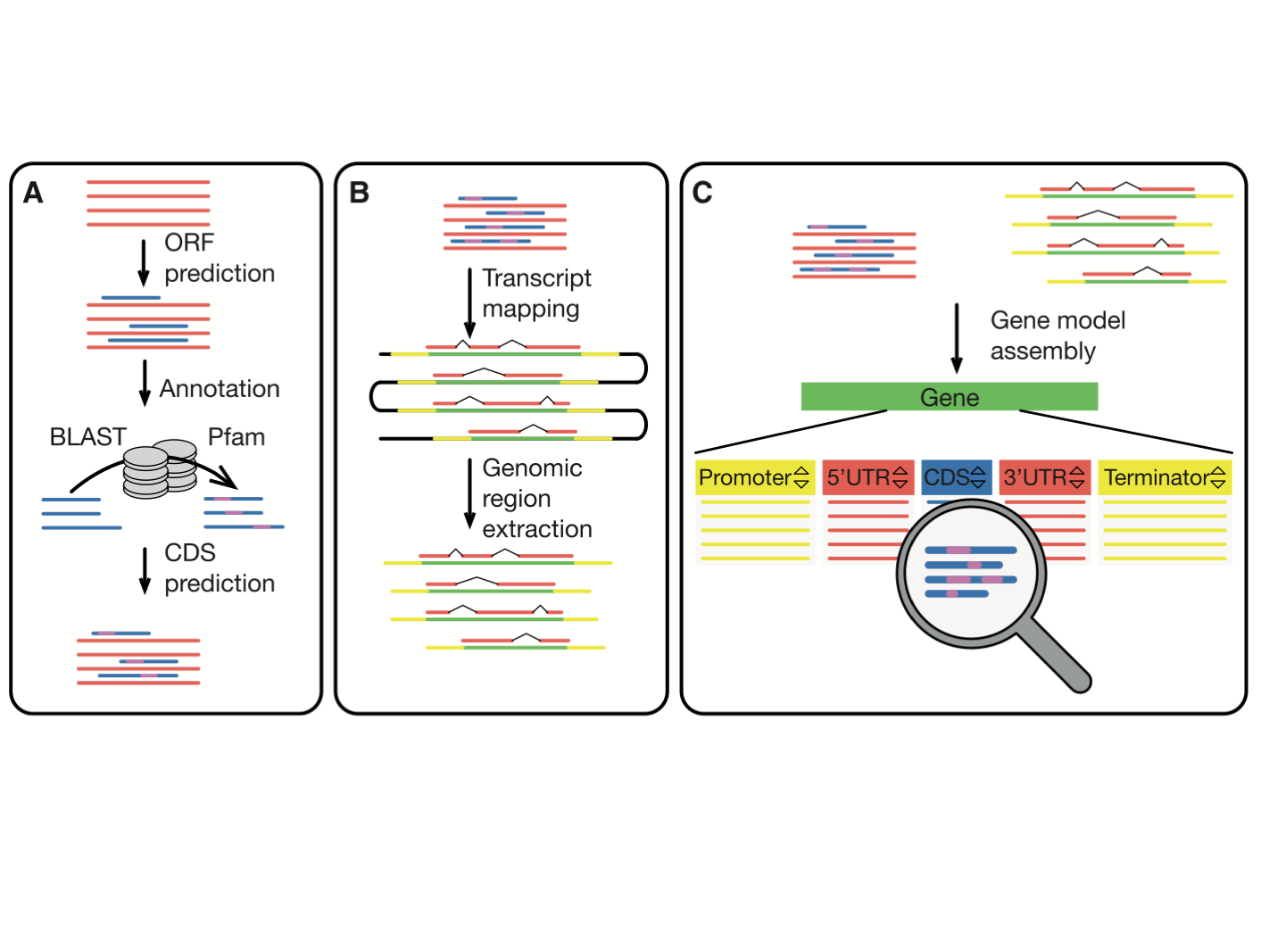
MarpoDB (Delmans et al, 2017) is a gene-centric database for Marchantia polymorpha Cam-1 strain genetic parts designed for genetic engineering and synthetic biology purposes constructed by Bernardo Pollak and Mihails Delmans in Jim Haseloff Lab. In version 3 of MarpoDB there are about 13,000 loci identified. You can BLAST to MarpoDB and HMMER to MarpoDB, and you can now search the database with Phytozome ID (ticking "DBxref" button).
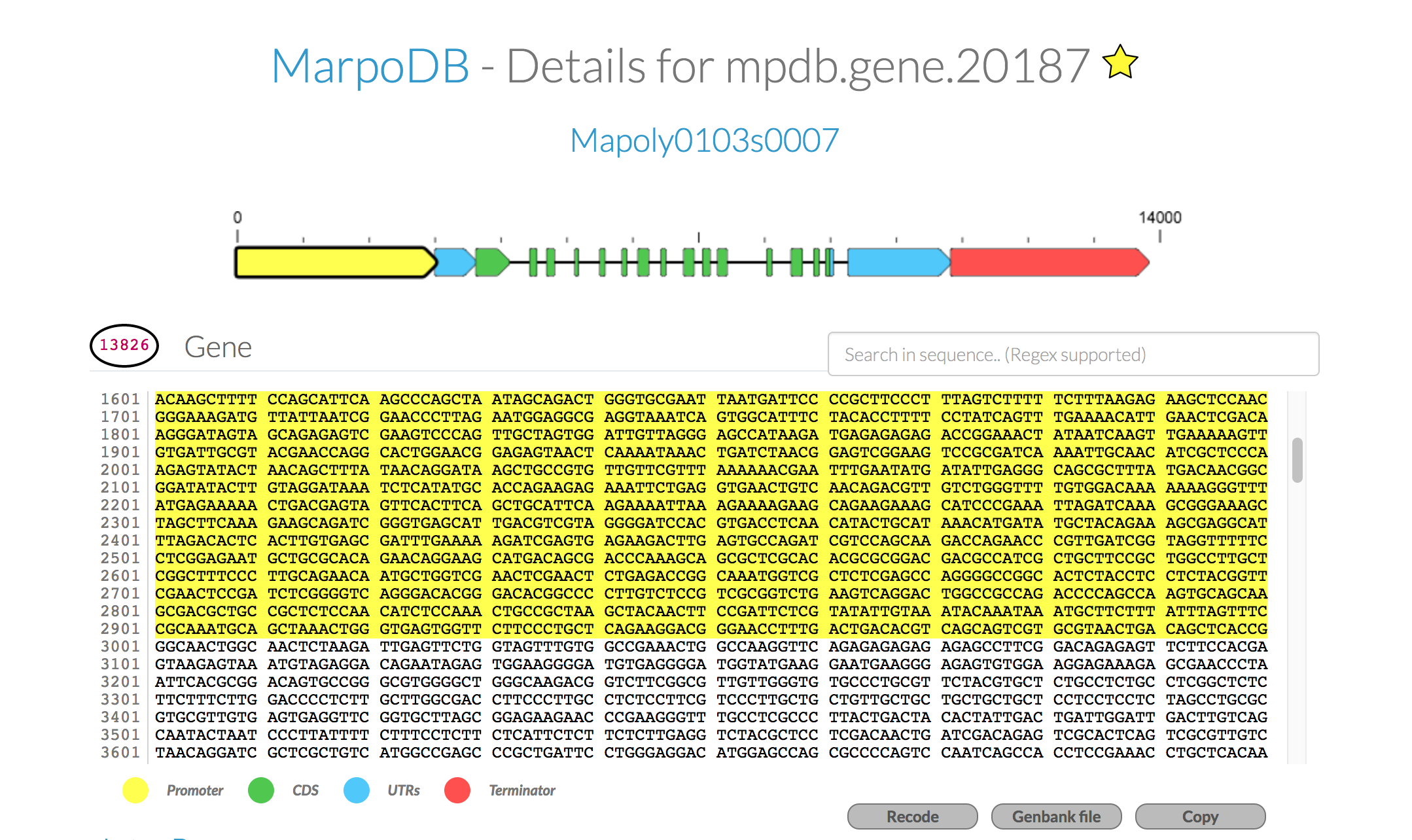
For each gene you'll find the genomic sequence of the genes, 5UTR-CDS-3UTR with exons and intons, as well as 3kb upstream and downstream for promoter elements and terminator sequences. To export the sequence with annotations, click the "genebank file" button at the bottom. This tool makes it easy to use the database to extract DNA parts for modular and standardised DNA assembly.
Nomenclature
The paper by Bowman et al. “The Naming of Names: Guidelines for Gene Nomenclature in Marchantia.” (2016), outlines community guidelines for M. polymorpha gene and transgene nomenclature, to promote consistency and reduce both redundancy and confusion in the scientific literature.
More details in Marchantia nomenclature



